IPsec Support
The vEOS Router provides robust support for the use of IPsec to establish and maintain IPsec tunnels for secure or encrypted communications between virtual router peer instances as well as virtual peer instances to non-virtual routers.
- Secure the communications between vEOS Router instances.
- Secure the communications between vEOS Router instances and third party virtual router instances.
- Supported Tunnel Types
The vEOS Router supports the use of two basic types of IPsec tunnels. The tunnel types are determined based on the encapsulation mode.
- Requirements when Behind a NAT
The vEOS Router supports the use of NAT-Traversal to communicate with the remote peer virtual router. To ensure that the tunnel configuration between the vEOS Router and peer router is successful, make sure that vEOS Router tunnel configuration meets the requirements for using NAT.
Note: NAT-Traversal for IPsec is not supported for DCS-7020SRG. - Using IPsec on CloudEOS and vEOS Router Instances
The vEOS Router enables you to establish and maintain GRE-over-IPsec and VTI IPsec tunnels for secure or encrypted communications between peer vEOS Router instances.
- Using IPsec on CloudEOS and vEOS and Third Party Devices
The vEOS Router enables you to establish and maintain IPsec tunnels for secure or encrypted communications between vEOS Router instances and third party peer router instances.
- CloudEOS IPsec Connectivity to Azure Virtual Network Gateway
Supported Tunnel Types
The CloudEOS and vEOS Router supports the use of two basic types of IPsec tunnels. The tunnel types are determined based on the encapsulation mode.
The supported tunnel types are:GRE-over-IPsec
- In GRE-over-IPsec encapsulation mode, the application payload is first encapsulated within a GRE packet. IPsec then encrypts the GRE packet, which results in the packet being encapsulated and encrypted by the IPsec header.
- Select this encapsulation type by specifying tunnel mode gre for the tunnel interface to which the IPsec profile is applied. This ensures that the packets forwarded on the interface are encrypted.
- When using GRE-over-IPsec encapsulation mode, both IPsec mode options are supported (select either transport or tunnel).
VTI IPsec
- In VTI encapsulation mode, the application payload is directly encapsulated and encrypted by the IPsec header.
- Select this encapsulation type by specifying tunnel mode ipsec for the tunnel interface to which the IPsec profile is applied. This ensures that the packets forwarded on the interface are encrypted.
- When using VTI encapsulation mode, set the IPsec mode to tunnel. The transport option under the IPsec mode has no effect.
Requirements when Behind a NAT
The CloudEOS and vEOS Router supports the use of NAT-Traversal to communicate with the remote peer behind a NAT. Configure the tunnel source with the outgoing interface IP address on the router.
Flow ParallelizationIf the IPsec session is established without the feature enabled, complete the following tasks:
- Under the IPsec profile for the tunnel use the flow parallelization encapsulation udp command to enable the feature.
- Shutdown the tunnel on the tunnel interface.
- Bring the tunnel back up on the tunnel interface. After it is up, this enables the feature.
Using IPsec on CloudEOS and vEOS Router Instances
Topology
Use the vEOS Router to establish and maintain IPsec tunnels between peer vEOS Router instances in different topologies of varying complexity.
The diagram below represents a basic IPsec tunnel configuration in which vEOS Router instances are using an IPsec tunnel.
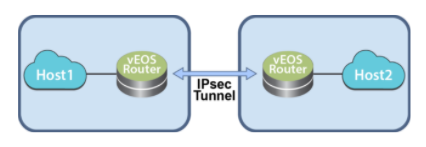
The vEOS Router establishes and maintains IPsec tunnels for secure or encrypted communications between vEOS Router instances and third party devices peer router instances.
- Creating IKE Policy for establishing IKE with the peer.
- Specifying the encryption, integrity protocols for the Security Association (SA) Policy.
- Apply IKE and SA policies to a given profile.
- Apply the profile to a tunnel interface.
Configuring IPsec Tunnels on CloudEOS and vEOS Router Instances
Use this procedure to configure GRE-over-IPsec or VTI IPsec tunnels on peer CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances.
The procedure provides all of the steps required to set up either GRE-over-IPsec or VTI IPsec tunnels. Most of the steps are the same for both tunnel types (steps 1 through 6 are the same). Step 7 is the step to select the tunnel type.
Procedure
Complete the following steps to configure GRE-over-IPsec or VTI IPsec tunnels on CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances. This configuration will be the default IKE version 2 procedure.
Examples of Running-configurations for GRE-over-IPsec Tunnels
The following examples show the running configurations for two CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances (CloudEOS and vEOS1 and CloudEOS and vEOS2). The instances are the tunnel endpoints of a GRE-over-IPsec tunnel.
Running Configuration for CloudEOS and vEOS1
ip security
ike policy ikebranch1
integrity sha256
dh-group 15
!
sa policy sabranch1
sa lifetime 2
pfs dh-group 14
!
profile hq
mode tunnel
ike-policy ikebranch1
sa-policy sabranch1
connection add
shared-key keyAristaHq
dpd 10 50 clear
!
interface Tunnel1
mtu 1404
ip address 1.0.3.1/24
tunnel mode gre
tunnel source 1.0.0.1
tunnel destination 1.0.0.2
tunnel ipsec profile hq
!
interface Ethernet1
no switchport
ip address 1.0.0.1/24
!Running Configuration for CloudEOS and vEOS2
ip security
ike policy ikebranch1
integrity sha256
dh-group 15
!
ike policy ikebranch2
dh-group 15
version 1
local-id 200.0.0.1
!
ike policy ikedefault
!
sa policy sabranch1
sa lifetime 2
pfs dh-group 14
!
profile hq
mode tunnel
ike-policy ikebranch1
sa-policy sabranch1
connection start
shared-key keyAristaHq
dpd 10 50 clear
!
interface Tunnel1
mtu 1404
ip address 1.0.3.2/24
tunnel mode gre
tunnel source 1.0.0.2
tunnel destination 1.0.0.1
tunnel ipsec profile hq
!
interface Ethernet2
no switchport
ip address 1.0.0.2/24
!Examples of Running-configurations for VTI IPsec Tunnels
The following examples show the running configurations for two CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances (CloudEOS and vEOS1 and CloudEOS and vEOS2). The instances are the tunnel endpoints of a VTI IPsec tunnel.
Running Configuration for CloudEOS and vEOS1
ip security
ike policy ikebranch1
integrity sha256
dh-group 15
!
sa policy sabranch1
sa lifetime 2
pfs dh-group 14
!
profile hq
mode tunnel
ike-policy ikebranch1
sa-policy sabranch1
connection add
shared-key keyAristaHq
dpd 10 50 clear
!
interface Ethernet1
no switchport
ip address 1.0.0.1/24
!
interface Management1
ip address dhcp
!
interface Tunnel1
mtu 1404
ip address 1.0.3.1/24
tunnel mode ipsec
tunnel source 1.0.0.1
tunnel destination 1.0.0.2
tunnel ipsec profile hq
!Running Configuration for CloudEOS and vEOS2
ip security
ike policy ikebranch1
integrity sha256
dh-group 15
!
ike policy ikebranch2
dh-group 15
version 1
local-id 200.0.0.1
!
ike policy ikedefault
!
sa policy sabranch1
sa lifetime 2
pfs dh-group 14
!
profile hq
mode tunnel
ike-policy ikebranch1
sa-policy sabranch1
connection start
shared-key keyAristaHq
dpd 10 50 clear
!
interface Ethernet2
no switchport
ip address 1.0.0.2/24
!
interface Management1 ip address dhcp
!
interface Tunnel1
mtu 1404
ip address 1.0.3.2/24
tunnel mode ipsec
tunnel source 1.0.0.2
tunnel destination 1.0.0.1
tunnel ipsec profile hq
!Using IPsec on CloudEOS and vEOS and Third Party Devices
The CloudEOS and vEOS Router establishes and maintains IPsec tunnels for secure or encrypted communications between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and third party devices peer router instances.
- Creating IKE Policy for establishing IKE with the peer.
- Specifying the encryption, integrity protocols for the Security Association (SA) Policy.
- Apply IKE and SA policies to a given profile.
- Apply the profile to a tunnel interface.
Topology
Use the vEOS Router to establish and maintain IPsec tunnels between vEOS Router instances and third party router instances in different topologies of varying complexity.
The following diagram represents a basic IPsec tunnel configuration in where a vEOS Router instance and a third party router instance is connected using an IPsec tunnel.

Interoperability Support
The CloudEOS and vEOS Router establishes and maintains IPsec tunnels for the secure or encrypted communications between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and third party device peer router instances.
- Palo Alto Firewall VM
- Set up these types of IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and Palo Alto firewall VM router instances.
- VTI IPsec
- Set up these types of IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and Palo Alto firewall VM router instances.
- CSR
- Set up these types of IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and CSR router instances.
- GRE-over-IPsec
- VTI IPsec
- Set up these types of IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and CSR router instances.
- AWS VPN Specific Cloud
- Set up these types of IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and AWS VPN Specific Cloud router instances.
- VTI IPsec
- Set up these types of IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and AWS VPN Specific Cloud router instances.
- vSRX
- Set up these types of IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and vSRX router instances.
- VTI IPsec
- Set up these types of IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and vSRX router instances.
CloudEOS and vEOS Router and Palo Alto Firewall VM
CloudEOS and vEOS Router Configuration
Use this procedure to configure GRE-over-IPsec tunnels on a CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance. Once the procedure is complete, configure the other tunnel end-point on the third party peer router.
Procedure
Complete the following steps to configure the CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance to share a GRE-over IPsec tunnel.
switch(config)#ip security
switch(config-ipsec)#ike policy ike-peerRtr
switch(config-ipsec-ike)#version 1Configuring VTI IPsec Tunnels
The CloudEOS and vEOS Router gives the ability to configure VTI IPsec tunnels between a CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance and a third party peer router instance (such as a Palo Alto firewall VM). First, complete the set up of the tunnel on the CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance, then set up the other end of the tunnel on the third party peer router instance.
Palo Alto Firewall VM Configuration
Use this configuration when pairing a Palo Alto firewall VM instance and CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance as tunnel endpoints of an IPsec VTI IPsec tunnel.
Supported Tunnel Types
Set up IPsec VTI tunnels when using the Palo Alto firewall VM as a peer router instance with a CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance. IPsec GRE-over-IPsec tunnels using this combination of router instances as peers is not permitted.
Configuration Guidelines
The following are guidelines to follow when configuring the Palo Alto firewall VM.
- IP address settings.
Configure the first interface to be configured (typically named eth0), as the management interface. Use the public IP address on this interface to open the GUI of the Palo Alto firewall VM.
- Management interface.
Use this interface only for control plane traffic.
- Management profile.
When configuring the profile, select all of the protocols allowed on the management interface.
Procedure
CloudEOS and vEOS and Palo Alto Firewall VM Pairing (VTI IPsec Tunnel)
The following example shows a VTI IPsec tunnel between a CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance and a third party Palo Alto firewall VM router instance.
Running Configuration for CloudEOS and vEOS1
ip security
ike policy ikebranch1
integrity sha256
dh-group 15
!
sa policy sabranch1
sa lifetime 2
pfs dh-group 14
!
profile hq
ike-policy ikebranch1
sa-policy sabranch1
connection add
shared-key keyAristaHq
dpd 10 50 clear
!
interface Ethernet1
no switchport
ip address 1.0.0.1/24
!
interface Management1
ip address dhcp
!
interface Tunnel1
mtu 1404
ip address 1.0.3.1/24
tunnel mode ipsec
tunnel source 1.0.0.1
tunnel destination 1.0.0.2
tunnel ipsec profile hq
!Running Configuration on Palo Alto Firewall VM
"ike": {
"crypto-profiles": {
"ike-crypto-profiles": [
{
"@name": "veos12-IKE-Phase1",
"hash": {
"member": "sha512"
},
"dh-group": {
"member": "group20"
},
"encryption": {
"member": "aes-256-cbc"
},
"lifetime": {
"hours": "8"
}
}
]
"ipsec-crypto-profiles": [
{
"@name": "veos12-IPSEC-Phase2",
"esp": {
"authentication": {
"member": "sha256"
},
"encryption": {
"member": "aes-256-cbc"
}
},
"lifetime": {
"hours": "2"
},
"dh-group": "group20"
}
"gateway": {
"entry": {
"@name": "veos12-IKE-Gateway",
"authentication": {
"pre-shared-key": {
"key": "-AQ==ocHnGzxJ4JVLomPyHuZNlg84S7I=BCiu0HIvFeFOSQOx/gmhNQ=="
}
},
"protocol": {
"ikev1": {
"dpd": {
"enable": "yes",
"interval": "100",
"retry": "100"
},
"ike-crypto-profile": "veos12-IKE-Phase1"
},
"ikev2": {
"dpd": {
"enable": "yes"
},
"ike-crypto-profile": "veos12-IKE-Phase1"
},
"version": "ikev2-preferred"
}
"tunnel": {
"ipsec": {
"entry": {
"@name": "veos12-IPSEC-Tunnel",
"auto-key": {
"ike-gateway": {
"entry": {
"@name": "veos12-IKE-Gateway"
}
},
"ipsec-crypto-profile": "veos12-IPSEC-Phase2"
},
"tunnel-monitor": {
"enable": "yes",
"destination-ip": "1.0.3.1",
"tunnel-monitor-profile": "Test"
},
"tunnel-interface": "tunnel.1",
"disabled": "no"
}
}
}
}CloudEOS and vEOS Router Configuration
Use this procedure to configure VTI IPsec tunnels on an Arista router instance. Complete the procedure, then configure the other tunnel endpoint on the third party peer router.
Procedure
Complete the following steps to configure a CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance to share a VTI IPsec tunnel.
To use IKE version 1, complete the section below, then continue with the steps below. To use IKE version 2, which is the default version, start with Step 1 below.
switch(config)#ip security
switch(config-ipsec)#ike policy ike-peerRtr
switch(config-ipsec-ike)#version 1Configure the VTI IPsec tunnel on the peer router (see Palo Alto Firewall VM Configuration).
CSR Router Show Commands
Describes the available CSR Router show commands and their example outputs.
- View all Existing ISAKMP SAs
- View all Existing IPsec SAs
- View Crypto (Encryption) Session Details
- View IKEv2 SAs
- View IKEv2 SA Details
View all Existing ISAKMP SAs
Use the show crypto isakmp sa command to view the ISAKMP SAs for all existing or current IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto isakmp sa
IPv4 Crypto ISAKMP SA
dstsrc state conn-id status
1.0.0.11.0.0.2 QM_IDLE 1331 ACTIVE
vrouter-ikev1-isakmp-profile
IPv6 Crypto ISAKMP SAView all Existing IPsec SAs
Use the show crypto ipsec sa command to view the IPsec SAs for all existing or current IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto ipsec sa
interface: Tunnel0
Crypto map tag: Tunnel0-head-0, local addr1.0.0.2
protected vrf: (none)
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port):
(1.0.0.2/255.255.255.255/47/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port):
(1.0.0.1/255.255.255.255/47/0)
current_peer 1.0.0.1 port 500
PERMIT, flags={origin_is_acl,}
#pkts encaps: 1, #pkts encrypt: 1, #pkts digest:1f
#pkts decaps: 1, #pkts decrypt: 1, #pkts verify:1
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed:0
#pkts not decompressed: 0, #pkts decompress failed:0
#send errors 0, #recv errors 0
local crypto endpt.: 1.0.0.2, remote crypto endpt.:
1.0.0.1
plaintext mtu 1438, path mtu 1500, ip mtu 1500, ip mtu idb
GigabitEthernet2
current outbound spi: 0xCB8FB740(3415193408)
PFS (Y/N): N, DH group: none
Dummy packet: Initializing
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0x36383677(909653623)
transform: esp-aes esp-sha-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
conn id: 5287, flow_id: CSR:3287, sibling_flags
FFFFFFFF80004048, crypto map: Tunnel0-head-0
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec):(4607999/3598)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Status: ACTIVE(ACTIVE)
inbound ah sas:
inbound pcp sas:
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0xCB8FB740(3415193408)
transform: esp-aes esp-sha-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
conn id: 5288, flow_id: CSR:3288, sibling_flags
FFFFFFFF80004048, crypto map: Tunnel0-head-0
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec):(4607999/3598)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support : Y
Status: ACTIVE(ACTIVE)
outbound ah sas:
outbound pcp sas:View Crypto (Encryption) Session Details
Use the show crypto session detail command to view details about the crypto session for all current IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto session detail
Crypto session current status
Code: C - IKE Configuration mode, D - Dead Peer Detection
K - Keepalives, N - NAT-traversal, T - cTCP encapsulation
X - IKE Extended Authentication, F - IKE Fragmentation
R - IKE Auto Reconnect
Interface: Tunnel0
Profile: vrouter-ikev1-isakmp-profile
Uptime: 00:20:23
Session status: UP-ACTIVE
Peer: 1.0.0.1 port 500 fvrf: (none) ivrf: (none)
Phase1_id: 1.0.0.1
Desc: (none)
Session ID: 0
IKEv1 SA: local 1.0.0.2/500 remote 1.0.0.1/500 Active
Capabilities:(none) connid:1332 lifetime:07:39:35
IPSEC FLOW: permit 47 host 1.0.0.2 host 1.0.0.1
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
Inbound: #pkts dec'ed 42 drop 0 life (KB/Sec)
4607997/2375
Outbound: #pkts enc'ed 44 drop 0 life (KB/Sec)
4607995/2375View IKEv2 SAs
Use the show crypto ikev2 sa command to view summary information about all IKE version 2 SAs in use by existing IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto ikev2 sa
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2SA
Tunnel-id Local Remotefvrf/ivrfStatus
1 3.3.3.3/500 3.3.3.1/500 none/noneREADY
Encr: AES-CBC, keysize: 128, PRF: sha256, Hash: SHA96,
DH Grp:14, Auth sign: PSK, Auth verify: PSK
Life/Active Time: 86400/5349 sec
IPv6 Crypto IKEv2SAView IKEv2 SA Details
Use the show crypto ikev2 sa detailed command to view details about all IKE version 2 SAs in use by existing IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto ikev2 sa detailed
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2 SA
Tunnel-id Local Remotefvrf/ivrfStatus
1 3.3.3.3/500 3.3.3.1/500 none/noneREADY
Encr: AES-CBC, keysize: 128, PRF: sha256, Hash: SHA96,
DH Grp:14, Auth sign: PSK, Auth verify: PSK
Life/Active Time: 86400/5358 sec
CE id: 1351, Session-id: 6
Status Description: Negotiation done
Local spi: 9FA0B7B1F7746E69 Remote spi:
4B1652D32691E8AF
Local id: 3.3.3.3
Remote id: 3.3.3.1
Local req msg id: 4Remote req msg id: 8
Local next msg id:4Remote next msg id:8
Local req queued: 4Remote req queued: 8
Local window: 5Remote window: 1
DPD configured for 0 seconds, retry 0
Fragmentation not configured.
Extended Authentication not configured.
NAT-T is not detected
Cisco Trust Security SGT is disabled
Initiator of SA : Yes
IPv6 Crypto IKEv2 SAIPsec Show Commands
The CloudEOS and vEOS Router provides commands to view all current or established IPsec tunnels and to view all profiles currently in use by established tunnels.
- show ip security connection
- show ip security connection detail
Examples
switch#show ip security connection
Tunnel SourceDest Status Uptime
Tunnel01.0.0.1 1.0.0.2Established14 minutes
Input OutputReauth Time
589 bytes 608 bytes 8 hours
7 pkts36 pktsswitch#show ip security connection detail
source address 1.0.0.1, dest address 1.0.0.2
Inbound SPI 0x672F6CC3:
request id 1, mode transport replay-window 32, seq 0x0
stats errors:
replay-window 0, replay 0, integrity_failed 0
lifetime config:
softlimit 18446744073709551615 bytes, hardlimit 18446744073709551615 bytes
softlimit 18446744073709551615 pkts, hardlimit 18446744073709551615 pkts
expire add 0 secs, hard 0 secs
lifetime current:
589 bytes, 7 pkts
add time Wed Aug 17 17:50:28 2016, use time Wed Aug 17 17:50:31 2016
Outbound SPI 0xc5f3c373:
request id 1, mode transport replay-window 32, seq 0x0
stats errors:
replay-window 0, replay 0, integrity_failed 0
lifetime config:
softlimit 18446744073709551615 bytes, hardlimit 18446744073709551615 bytes
softlimit 18446744073709551615 pkts, hardlimit 18446744073709551615 pkts
expire add 0 secs, hard 0 secs
lifetime current:
608 bytes, 7 pkts
add time Wed Aug 17 17:50:28 2016, use time Wed Aug 17 17:50:31 2016switch#show ip sec applied-profile
Profile Name Interface
Arista Tunnel0CloudEOS and vEOS Routers and CSR
Use this configuration process to set up GRE-over-IPsec tunnels on CSR peer routers. Procedures are provided for configuration using IKE version 1, or IKE version 2. Make sure to use the correct procedure based on the selected version of IKE.
CSR Configuration
The configuration of VTI IPsec tunnels on CSR peer router instances is almost identical to the configuration of GRE-over-IPsec tunnels on CSR peer router instances. The only difference in the configurations is tunnel mode.
For VTI IPsec tunnels, tunnel mode must be set to ipsec instead of gre (for GRE-over-IPsec tunnels, tunnel mode must be set to gre.)
This example shows a basic VTI IPsec tunnel configuration for a CSR peer router instance.
Example
switch(config)#interface Tunnel0
switch(config-if)#ip address 1.0.3.1 255.255.255.0
switch(config-if)#tunnel source 10.3.31.30
switch(config-if)#tunnel destination 10.2.201.149
switch(config-if)#tunnel mode ipsec ipv4
switch(config-if)#tunnel protection ipsec profile vrouter-ikev1-ipsec-profileSharing IPsec Connections
On CSR, the user can configure multiple GRE tunnels to use the same IPsec connection.
switch(config)#interface Tunnel0
switch(config-if)#tunnel protection ipsec profile vrouter-ikev2-ipsec-profile shared
switch(config-if)#exitIKEv1 Configuration
The CSR configuration to create a GRE over IPsec tunnel is similar the CloudEOS and vEOS Router setup using ikev1 version.
switch(config)#ip security
switch(config-ipsec)#ike policy ike-peerRtr
switch(config-ipsec-ike)#version 1IKEv2 Configuration
The CSR configuration to create a GRE over IPsec tunnel is similar to the CloudEOS and vEOS Router setup using ikev2 version.
By default, the CloudEOS and vEOS Router is configured to run in IKEv2 version. Make sure the version is not set to 1 under the ike policy. The configuration steps for CSR IKEv2 are a bit different to that of IKEv1.
Complete the following steps to configure the CSR.
CloudEOS and vEOS Router (GRE-over-IPsec Tunnel)
The IPsec tunnels represented in these examples include GRE-over-IPsec tunnels on CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances.
Running Configuration for CloudEOS and vEOS
ip security
ike policy ikebranch1 encryption aes256 dh-group 15
!
sa policy sabranch1 sa lifetime 2
pfs dh-group 14
!
profile hq
ike-policy ikebranch1 sa-policy sabranch1 connection add
shared-key keyAristaHq dpd 10 50 clear
!
interface Tunnel1
ip address 1.0.3.1/24 tunnel mode gre tunnel source 1.0.0.1
tunnel destination 1.0.0.2 tunnel ipsec profile hq
interface Ethernet1 no switchport
ip address 1.0.0.1/24CloudEOS and vEOS Router (VTI IPsec Tunnel)
The IPsec tunnels represented in these examples include VTI IPsec tunnels between CloudEOS and vEOS Router instances and third party CSR router instances.
Running Configuration for CloudEOS and vEOS
ip security
ike policy ikebranch1
encryption aes256
dh-group 15
!
sa policy sabranch1
sa lifetime 2
pfs dh-group 14
!
profile hq
ike-policy ikebranch1
sa-policy sabranch1
connection add
shared-key keyAristaHq
dpd 10 50 clear
!
interface Tunnel1
ip address 1.0.3.1/24
tunnel mode ipsec
tunnel source 1.0.0.1
tunnel destination 1.0.0.2
tunnel key 100
tunnel ipsec profile hq
interface Ethernet1
no switchport
ip address 1.0.0.1/24CSR Commands
The CSR router has show commands for several IPsec tunnel elements on CSR router instances.
CSR Router Show Commands
Describes the available CSR Router show commands and their example outputs.
- View all Existing ISAKMP SAs
- View all Existing IPsec SAs
- View Crypto (Encryption) Session Details
- View IKEv2 SAs
- View IKEv2 SA Details
View all Existing ISAKMP SAs
Use the show crypto isakmp sa command to view the ISAKMP SAs for all existing or current IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto isakmp sa
IPv4 Crypto ISAKMP SA
dstsrc state conn-id status
1.0.0.11.0.0.2 QM_IDLE 1331 ACTIVE
vrouter-ikev1-isakmp-profile
IPv6 Crypto ISAKMP SAView all Existing IPsec SAs
Use the show crypto ipsec sa command to view the IPsec SAs for all existing or current IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto ipsec sa
interface: Tunnel0
Crypto map tag: Tunnel0-head-0, local addr1.0.0.2
protected vrf: (none)
local ident (addr/mask/prot/port):
(1.0.0.2/255.255.255.255/47/0)
remote ident (addr/mask/prot/port):
(1.0.0.1/255.255.255.255/47/0)
current_peer 1.0.0.1 port 500
PERMIT, flags={origin_is_acl,}
#pkts encaps: 1, #pkts encrypt: 1, #pkts digest:1f
#pkts decaps: 1, #pkts decrypt: 1, #pkts verify:1
#pkts compressed: 0, #pkts decompressed: 0
#pkts not compressed: 0, #pkts compr. failed:0
#pkts not decompressed: 0, #pkts decompress failed:0
#send errors 0, #recv errors 0
local crypto endpt.: 1.0.0.2, remote crypto endpt.:
1.0.0.1
plaintext mtu 1438, path mtu 1500, ip mtu 1500, ip mtu idb
GigabitEthernet2
current outbound spi: 0xCB8FB740(3415193408)
PFS (Y/N): N, DH group: none
Dummy packet: Initializing
inbound esp sas:
spi: 0x36383677(909653623)
transform: esp-aes esp-sha-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
conn id: 5287, flow_id: CSR:3287, sibling_flags
FFFFFFFF80004048, crypto map: Tunnel0-head-0
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec):(4607999/3598)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support: Y
Status: ACTIVE(ACTIVE)
inbound ah sas:
inbound pcp sas:
outbound esp sas:
spi: 0xCB8FB740(3415193408)
transform: esp-aes esp-sha-hmac ,
in use settings ={Tunnel, }
conn id: 5288, flow_id: CSR:3288, sibling_flags
FFFFFFFF80004048, crypto map: Tunnel0-head-0
sa timing: remaining key lifetime (k/sec):(4607999/3598)
IV size: 16 bytes
replay detection support : Y
Status: ACTIVE(ACTIVE)
outbound ah sas:
outbound pcp sas:View Crypto (Encryption) Session Details
Use the show crypto session detail command to view details about the crypto session for all current IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto session detail
Crypto session current status
Code: C - IKE Configuration mode, D - Dead Peer Detection
K - Keepalives, N - NAT-traversal, T - cTCP encapsulation
X - IKE Extended Authentication, F - IKE Fragmentation
R - IKE Auto Reconnect
Interface: Tunnel0
Profile: vrouter-ikev1-isakmp-profile
Uptime: 00:20:23
Session status: UP-ACTIVE
Peer: 1.0.0.1 port 500 fvrf: (none) ivrf: (none)
Phase1_id: 1.0.0.1
Desc: (none)
Session ID: 0
IKEv1 SA: local 1.0.0.2/500 remote 1.0.0.1/500 Active
Capabilities:(none) connid:1332 lifetime:07:39:35
IPSEC FLOW: permit 47 host 1.0.0.2 host 1.0.0.1
Active SAs: 2, origin: crypto map
Inbound: #pkts dec'ed 42 drop 0 life (KB/Sec)
4607997/2375
Outbound: #pkts enc'ed 44 drop 0 life (KB/Sec)
4607995/2375View IKEv2 SAs
Use the show crypto ikev2 sa command to view summary information about all IKE version 2 SAs in use by existing IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto ikev2 sa
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2SA
Tunnel-id Local Remotefvrf/ivrfStatus
1 3.3.3.3/500 3.3.3.1/500 none/noneREADY
Encr: AES-CBC, keysize: 128, PRF: sha256, Hash: SHA96,
DH Grp:14, Auth sign: PSK, Auth verify: PSK
Life/Active Time: 86400/5349 sec
IPv6 Crypto IKEv2SAView IKEv2 SA Details
Use the show crypto ikev2 sa detailed command to view details about all IKE version 2 SAs in use by existing IPsec connections.
Example
switch#show crypto ikev2 sa detailed
IPv4 Crypto IKEv2 SA
Tunnel-id Local Remotefvrf/ivrfStatus
1 3.3.3.3/500 3.3.3.1/500 none/noneREADY
Encr: AES-CBC, keysize: 128, PRF: sha256, Hash: SHA96,
DH Grp:14, Auth sign: PSK, Auth verify: PSK
Life/Active Time: 86400/5358 sec
CE id: 1351, Session-id: 6
Status Description: Negotiation done
Local spi: 9FA0B7B1F7746E69 Remote spi:
4B1652D32691E8AF
Local id: 3.3.3.3
Remote id: 3.3.3.1
Local req msg id: 4Remote req msg id: 8
Local next msg id:4Remote next msg id:8
Local req queued: 4Remote req queued: 8
Local window: 5Remote window: 1
DPD configured for 0 seconds, retry 0
Fragmentation not configured.
Extended Authentication not configured.
NAT-T is not detected
Cisco Trust Security SGT is disabled
Initiator of SA : Yes
IPv6 Crypto IKEv2 SACloudEOS and vEOS Routers and AWS Specific Cloud Configuration
Describes the configuration steps for an AWS specific cloud on a CloudEOS and vEOS Router instance.
IPsec Between the CloudEOS and vEOS Router and AWS Specific Cloud Configuration
Describes the steps and the running configuration for setting up an IPsec connection between the CloudEOS and vEOS Router and the AWS Specific Cloud. The AWS Specific Cloud only supports IKE1 and not IKE2.
The following configurations are for the minimum requirement of AES128, SHA1, and DH Group 2. These can be modified to take advantage of AES256, SHA256, or other DH groups such as 5, 14-17, and 24.
Running-configuration of the CloudEOS and vEOS Router and AWS Specific Cloud
The sample configuration below sets up the running configuration of the CloudEOS and vEOS Router and AWS Specific Cloud. In the configuration, the local-id is the external IP of the router when it is behind a NAT device, and the tunnel destination is the external IP of the AWS Specific Cloud.
ip security
ike policy AWS-IKE1
integrity sha1
version 1
local-id 52.165.228.195
!
ike policy ikedefault
encryption aes256
!
sa policy AWS-SA1
esp encryption aes128
esp integrity sha1
pfs dh-group 14
!
profile AWS-profile
ike-policy AWS-IKE1
sa-policy AWS-SA1
connection start
sharded-key LwYbARmDJmpFGAOrAbPGk2uQiWwvbmfU
!
profile default
ike-policy
sa-policy AWS-SA1
shared-key arista
!
interface Tunnel1
ip address 169.254.11.162/30
tunnel mode ipsec
tunnel source 10.2.0.4
tunnel destination 52.53.75.160
tunnel ipsec profile AWS-profileAWS Specific Cloud Configuration
- Internet Key Exchange Configuration
- Authentication Method: Pre-Shared Key
- Pre-Shared Key: LwYbARmDJmpFGOrAbPGk2uQiWwvbmfU
- Authentication Algorithm: sha1
- Encryption Algorithm: aes-128-cbc
- Lifetime: 28800 seconds
- Phase 1 Negotiation Method: main
- Perfect Forward Secrecy: Diffie-Hellman Group 2
AWS Specific Cloud Configuration Modifications
- Internet Key Exchange SA Configuration
The address of the external interface for the customer gateway must be a static address. The customer gateway can reside behind a device performing Network Address Translation (NAT). To make sure that NAT traversal (NAT-T) functions correctly, add or update the firewall rule to allow UDP port 4500. Disable NAT-T if the customer gateway is not behind a NAT gateway.
Use the following sample configuration files to set up an Internet key exchange SA configuration.- Authentication Method: Pre-shared Key
- Pre-shard Key: LwYbARmDJmpFGAOrAbPGk2uQiWwvbmfU
- Authentication Algorithm: sha1
- Encryption Algorithm: aes-128-cbc
- Lifetime: 28800 seconds
- Phase 1 Negotiation Mode: main
- Perfect Forward Secrecy: Diffie-Hellman Group 2
- IPsec Configuration
Use the following sample configuration files to configure the IPsec. Modification of the sample configuration files may be need to take advantage of additionally supported IPsec parameters for encryption, such as AES256 and other DH groups like 2, 5, 14-18, 22, 23, and 24.
- Protocol: esp
- Authentication Algorithm: hmac-sha-96
- Encryption Algorithm: aes-128-cbc
- Lifetime: 3600 seconds
- Mode: tunnel
- Perfect Forward Secrecy: Diffie-Hellman Group2
The IPsec Dead Peer Detection (DPD) is enabled on the AWS Specific Cloud endpoint. Configure the DPD on your endpoint as follows:- DPD interval: 10
- DPD Retries: 3
The IPsec Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) inserts additional headers to transmit the packets. These headers require additional space, which reduces the amount of space available to transmit application data. The following configuration is recommended on the customer gateway to limit the impact of this behavior:
- TCP MSS Adjustment: 1379 bytes
- Clear Don't fragment Bit: enabled
- Fragmentation: Before encryption
- Tunnel Interface Configuration
Configure the customer gateway with a tunnel interface that associates with the IPsec tunnel. All traffic transmitted to the tunnel interface is encrypted and transmitted to the virtual private gateway.
The customer gate and the virtual private gateway each have two addresses that relate to this IPsec tunnel. Each one contains an outside address, where the encrypted traffic is exchanged. Both gateways also contain an inside address associated with the tunnel interface. The customer gateway outside IP address is provided upon creation of the customer gateway. To change the IP address of the customer gateway, create a new customer gateway. The customer gateway inside IP address must be configured on the interface tunnel.
Outside IP Addresses:- Customer Gateway: 52.165.228.195
- Virtual Private Gateway: 52.53.75.160
The customer gateway IP address is the IP address of the firewall that the CloudEOS and vEOS instance in the DC with NAT behind.
The virtual private gateway IP address is the external IP address of the AWS Specific Cloud.
Inside IP Addresses- Customer Gateway: 169.254.11.162/30
- Virtual Private Gateway: 169.254.11.161/30
The virtual private gateway IP address is the tunnel IP address of the AWS Specific Cloud.
- Static Routing Configuration
The router traffic between the internal network and the VPC an AWS Specific Cloud, add a static router to the CloudEOS and vEOS Router.
Next Hop: 169.254.11.162
Any subnet that requires a route to DC must have a route pointing to the AWS Specific Cloud tunnel IP address.
For traffic destined to the Internet Network, add static routes on the VGW.
CloudEOS IPsec Connectivity to Azure Virtual Network Gateway
This document describes how to establish IPsec connection between CloudEOS router and Azure Virtual Network Gateway. This document also documents how to establish a BGP connection over the IPsec tunnel.
Creating an IPsec Azure Virtual Network Gateway
The following topology is for IPsec Azure Virtual Network Gateway.

The following steps are to create an IPsec Azure Virtual Network Gateway.
- Create a Resource Group.
- Create the Virtual Network.
- Create Virtual Network Gateway.
- Configure Local Network Gateway.
- Create Site-to-site Connections.
For more information on creating an IPsec Azure Virtual Network Gateway, refer to:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/vpn-gateway/vpn-gateway-howto-site-to-site-resource-manager-portal
Creating a Resource Group

Creating a Virtual Network
Creating an Virtual Network Gateway
Configuring the Local Network Gateway
Creating Site-to-site Connections
A site-to-site connection is configured to connect a Virtual Network Gateway to the Local Network Gateway. In addition to this IKE version and shared-key used for IKE authentication is configured. The rest of the cryptographic parameters cannot be configured from the Azure portal, but can be configured using Power shell. The complete list of Azure crypto suites is found here:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/vpn-gateway/vpn-gateway-ipsecikepolicy-rm-powershell#params
Configuring CloudEOS IPsec
IKE - Ikev2/AES256/SHA256/DH-Group2
IPsec - ESP/AES256/SHA256Configure the IKE Policy
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-ike)#ip security
CloudEOS(config-ipsec)#ike policy ikeAzure
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-ike)#encryption aes256
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-ike)#integrity sha256
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-ike)#version 2
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-ike)#dh-group 2
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-ike)#ex
CloudEOS(config-ipsec)#Configure the SA Policy
CloudEOS(config-ipsec)#sa policy saAzure
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-sa)#esp encryption aes256
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-sa)#esp integrity sha256
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-sa)#ex
CloudEOS(config-ipsec)#Configure the Profile
CloudEOS(config-ipsec)#profile profAzure
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-profile)#ike-policy ikeAzure
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-profile)#sa-policy saAzure
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-profile)#connection start
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-profile)#shared-key arista
CloudEOS(config-ipsec-profile)#ex
CloudEOS(config-ipsec)#Configuring the IPsec Tunnel (VTI) Interface
CloudEOS(config)#interface Tunnel 1
CloudEOS(config-if-Tu1)#ip address 10.100.1.1/24
CloudEOS(config-if-Tu1)#tunnel mode ipsec
CloudEOS(config-if-Tu1)#tunnel source 3.212.212.81
CloudEOS(config-if-Tu1)#tunnel destination 13.77.139.173
CloudEOS(config-if-Tu1)#tunnel ipsec profile profAzure
! IPSec adds an overhead of up to 82 bytes. Example: A GRE tunnel with an MTU=1476 should be changed to 1394 when using IPSec.
CloudEOS(config-if-Tu1)#ex
CloudEOS(config)#showVerifying the IPsec Connection
CloudEOS(config)#show ip securityconnection
TunnelSourceDest Status UptimeInputOutput Rekey Time
Tunnel13.212.212.8113.77.139.173 Established1 second0 bytes0 bytes44 minutes
0 pkts 0 pkts 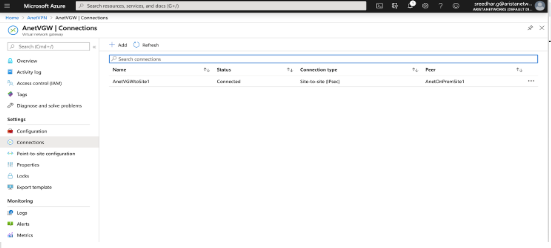
On Prem CloudEOS behind a NAT Device
CloudEOS#ip security
ike policy ikeAzure
encryption aes256
dh-group 2
local-id 3.212.212.81BGP over IPsec
CloudEOS(config)#router bgp 65530
CloudEOS(config-router-bgp)#neighbor 172.27.0.254 remote-as 65515
CloudEOS(config-router-bgp)#neighbor 172.27.0.254 update-source Tunnel1
CloudEOS(config-router-bgp)#neighbor 172.27.0.254 ebgp-multihop 4
CloudEOS(config-router-bgp)#address-family ipv4
CloudEOS(config-router-bgp-af)#neighbor 172.27.0.254 activate
CloudEOS(config-router-bgp-af)#network 10.100.100.0/24
CloudEOS(config-router-bgp-af)#ex
CloudEOS(config-router-bgp)#ex
CloudEOS(config)#BGP Routes Advertised to Neighbor
CloudEOS(config)#show ip bgpneighbors 172.27.0.254 advertised-routes
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 198.18.0.65, local AS number 65530
Route status codes: s - suppressed, * - valid, > - active, # - not installed, E - ECMP head, e - ECMP
S - Stale, c - Contributing to ECMP, b - backup, L - labeled-unicast, q - Queued for advertisement
% - Pending BGP convergence
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI Origin Validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, U - unknown
AS Path Attributes: Or-ID - Originator ID, C-LST - Cluster List, LL Nexthop - Link Local Nexthop
NetworkNext HopMetricLocPref WeightPath
* >10.100.100.0/2410.100.1.1- - - 65530 iBGP Routes Received from the Neighbor
CloudEOS(config)#show ip bgpneighbors 172.27.0.254received-routes
BGP routing table information for VRF default
Router identifier 198.18.0.65, local AS number 65530
Route status codes: s - suppressed, * - valid, > - active, # - not installed, E - ECMP head, e - ECMP
S - Stale, c - Contributing to ECMP, b - backup, L - labeled-unicast
% - Pending BGP convergence
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI Origin Validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, U - unknown
AS Path Attributes: Or-ID - Originator ID, C-LST - Cluster List, LL Nexthop - Link Local Nexthop
NetworkNext HopMetricLocPref WeightPath
* >172.27.0.0/16172.27.0.254- - - 65515 i
CloudEOS(config)#Verifying the BGP Connection
CloudEOS(config)#show ip bgp summ
BGP summary information for VRF default
Router identifier 198.18.0.65, local AS number 65530
Neighbor Status Codes: m - Under maintenance
Neighbor VAS MsgRcvd MsgSentInQ OutQUp/Down State PfxRcd PfxAcc
172.27.0.254 4655151942140 000:00:06Estab 11
CloudEOS(config)#














