Networks
Managing Networks in ETM Dashboard
ETM Dashboard enables you to group Edge Threat Management NG Firewall and Micro Edge appliances into a network. By grouping appliances, you can obtain information specific to the collection of appliances in the Network. You can also apply a standard set of WAN Routing Rules to all Micro Edge appliances that belong to the same Network.
Creating a Network
- Click the Networks tab. The Networks screen shows a list of your Networks.
- Click Create Network.
- Select the NG Firewall and Micro Edge appliances to add to your Network.
- Click Next to review the summary of your Network.
- Click Create.
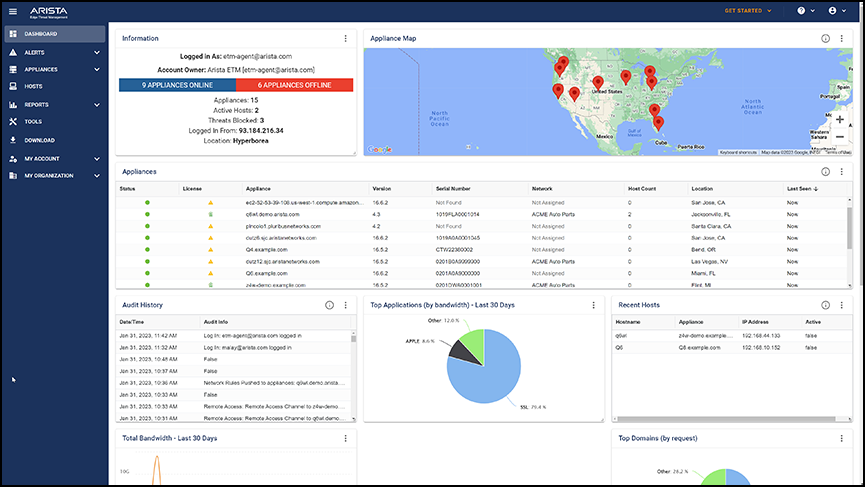
Managing Appliances in your Network
Your Networks appear in the Networks panel of the Networks screen. Select a Network to manage its associated appliances.
Appliances Widget
The Appliances widget shows the status, software version, location, IP address, and other relevant details of each appliance in your Network. You can add or remove appliances from your Network using the Add Appliance and Remove Appliance buttons at the bottom of the widget.
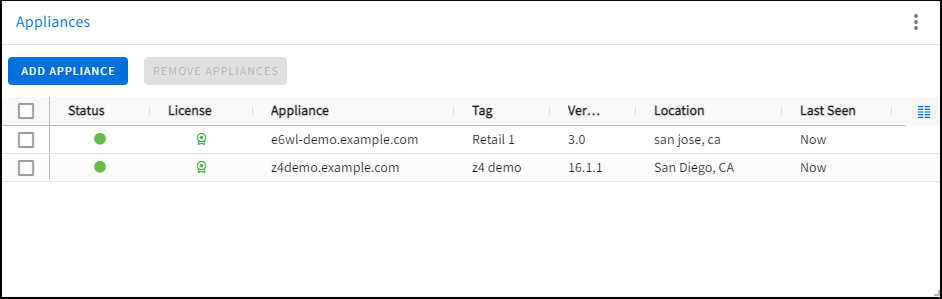
Select the filter options to locate an appliance in the list by clicking the three horizontal lines in any column header.
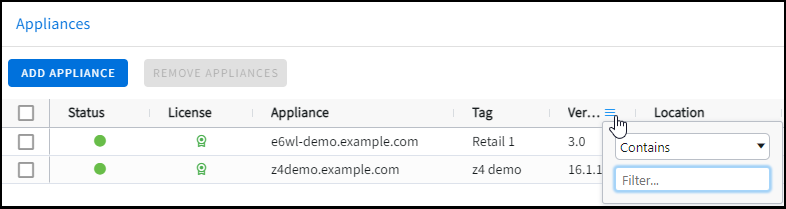
The grid menu provides additional options, including sorting and choosing columns to show or hide appliance properties.
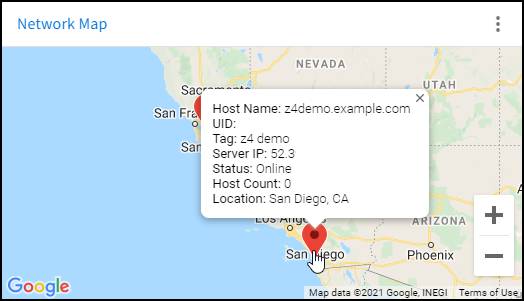
Map Widget
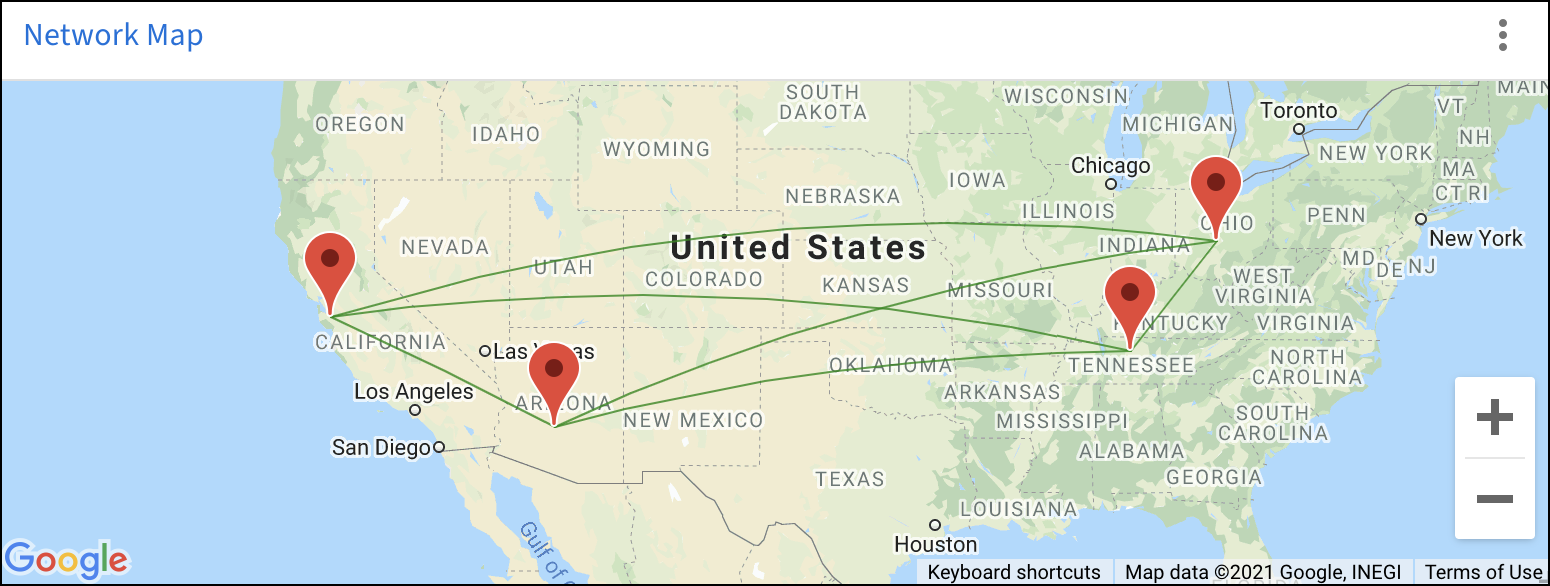
The Network Map widget displays the physical location of each appliance in your network. Hover over a marker to view additional details about the appliance, or click the marker to open the dashboard. If you enable appliances in Software-defined Networks, the map draws green or red lines between the markers to indicate the link status between each location.
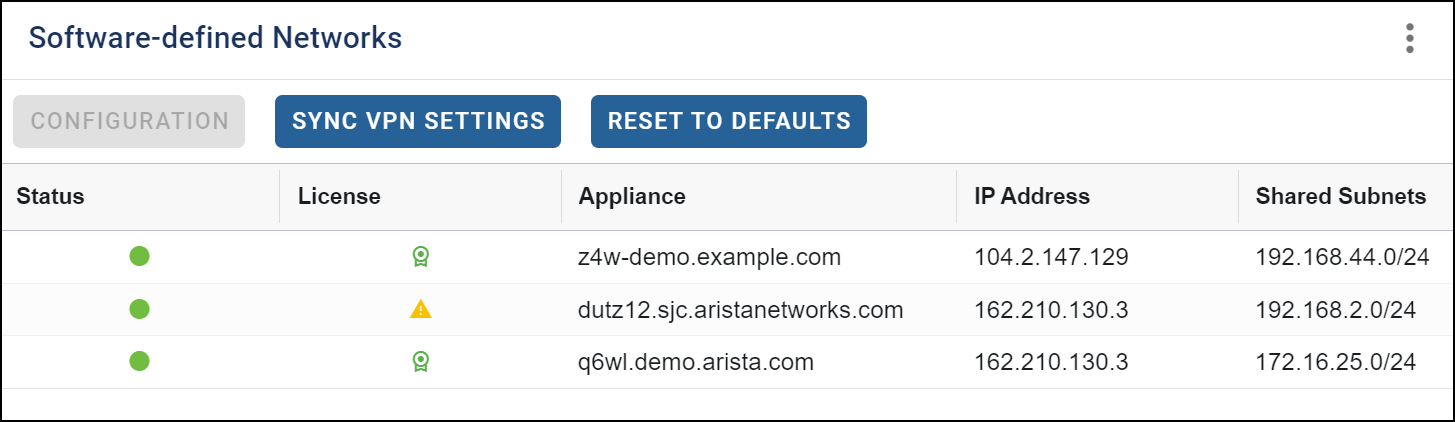
Software-defined Networks Widget
The Software-defined Networks widget enables you to configure a Virtual Private Network for appliances in the network. For more information on this widget, see Setting up Software-defined Networks in ETM Dashboard.
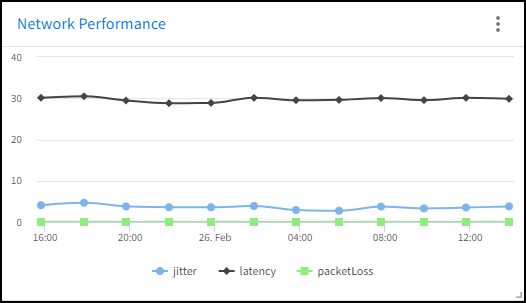
Network Performance Widget
The Network Performance widget displays the average jitter, latency, and packet loss across all Micro Edge appliances in your Network. Click any of the performance metrics in the legend to show or hide its view in the line chart.
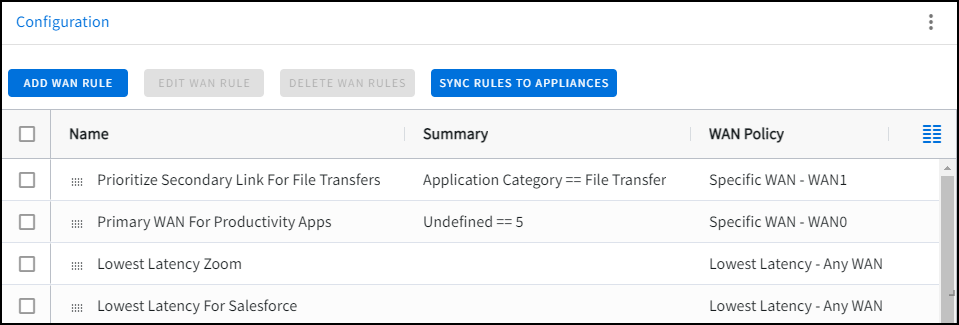
WAN Rules Widget
The WAN Rules widget establishes a common WAN Routing strategy for all Micro Edge appliances in your Network; for more information, see Configuring WAN Rules for Micro Edge in the ETM Dashboard.
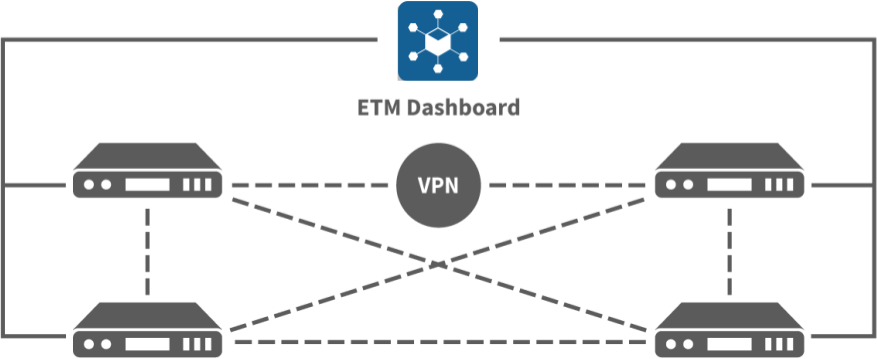
Setting up Software-defined Networks in the ETM Dashboard
You can automatically set up one or more software-defined networks to connect remote office networks managed by Micro Edge and NG Firewall. The ETM dashboard controls each software-defined network and uses WireGuard VPN tunnels to route traffic between each network in a site-to-site mesh topology. Managing your software-defined networks via ETM Dashboard reduces the complexity of manually configuring VPN tunnels.
Prerequisites
Before configuring your Software-defined network, confirm that your appliances meet the following requirements:
- Version 3.1 or newer
- Version 16.1 or newer.
- IPsec and OpenVPN must be disabled or uninstalled.
- NG Firewall Complete or Trial License.
- You must install the WireGuard app.
Setting up the Software-defined Network
To set up your software-defined network, you must first create one. See Managing Software-defined Networks in ETM Dashboard for steps to create your Software-defined Network.
- From the Networks list, select your network.
- Locate the Software Defined Network widget containing the appliances in your network.

- Select each appliance and click Configuration.
- Turn on the Enable option to activate VPN access for this appliance and the networks behind it.
- After enabling access, choose the local subnets you want to make accessible to other appliances in this network.
- You can also specify a new Endpoint Address if you would like to choose the WAN IP address used when other appliances connect to this appliance. You can enable the 'Automatic' option to allow the ETM Dashboard to determine the appropriate endpoint address.
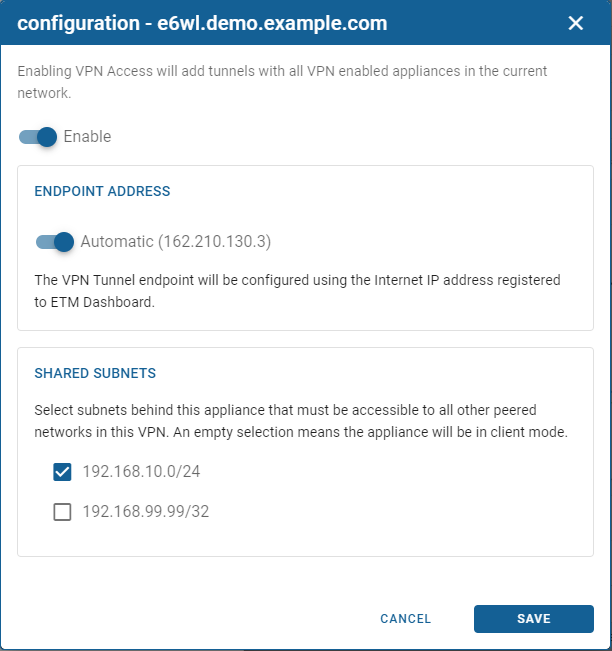
- Selecting shared subnets is optional. If no local subnets are enabled, this appliance network acts in client mode and can access resources of remote networks but not vice versa.
- If a local subnet conflicts with a shared subnet from a different appliance, you cannot enable VPN access, which may result in routing issues.
Synchronizing the Software-defined Network
After you enable access to your appliances and specify shared subnets, you must synchronize your changes. This action adds, removes, or updates VPN tunnels for each appliance in the network.
By clicking Sync VPN Settings, the ETM Dashboard queues the request for processing, which may take several minutes. You can review the Audit History to check the status of your sync request.

After synchronization, you can review the tunnels and their status by logging into each appliance.
Troubleshooting
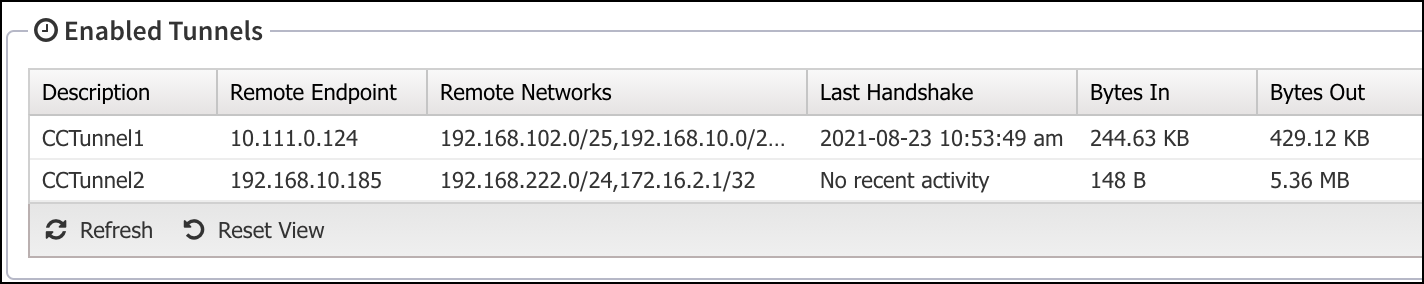
You confirm that the VPN tunnels are synchronized to an NG Firewall appliance; you can view the Enabled Tunnels grid on the WireGuard VPN Status page. The Last Handshake confirms the most recent successful transfer, and the Bytes In and Bytes Out ensure that data flows in both directions.
You can view the Interfaces screen to confirm that VPN tunnels are synchronized to a Micro Edge appliance. The Connected and Online statuses confirm that the tunnel is up, and the arrows confirm that data flows in both directions.
You can check the status of your Centrally Managed Network tunnels from the Network Dashboard. The Network Map shows the links between each peer in the network.
If there is a specific reason that an appliance cannot sync, the Software Defined Network widget provides information in the Notes column next to the associated appliance.
WireGuard VPN
The WireGuard VPN service provides virtual private networking via Wireguard VPN, an open-source lightweight VPN application and protocol designed to be fast, secure, and easy to configure.
Settings
This section reviews the different settings and configuration options available for WireGuard VPN.
Status
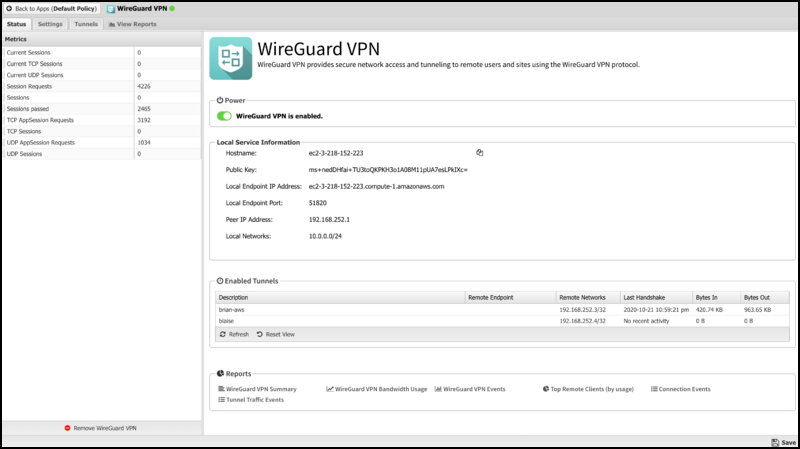
The Status tab shows the status of the WireGuard VPN service
- Local Service Information
This section displays information about the local WireGuard service, such as the public key, endpoint address and port, peer address, and the list of local networks.
- Enabled Tunnels
This section shows a list of active WireGuard tunnels.
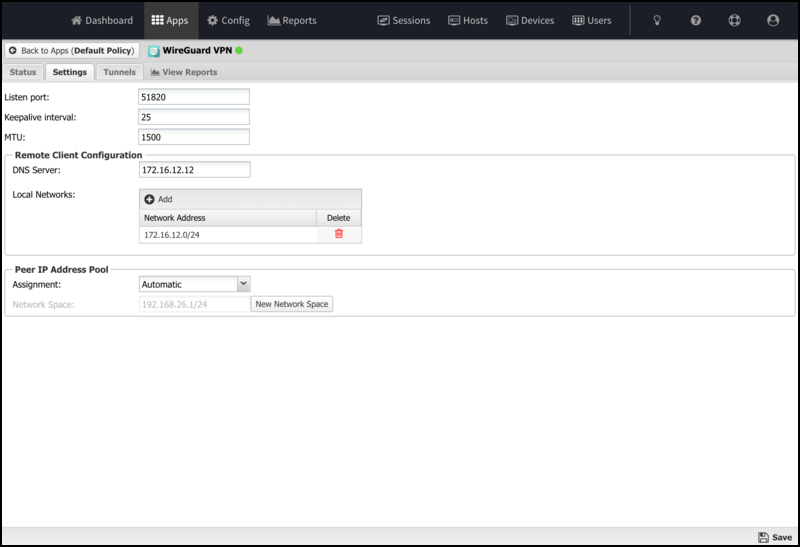
- Listen port
- Sets the port where the WireGuard server will listen for inbound tunnel connections from peers.
- Keepalive interval
- Sets the passive keepalive interval, which ensures that sessions stay active and allows both peers to determine if a connection has failed or been disconnected passively.
- MTU
- Sets the MTU size for WireGuard tunnels.
Remote Client Configuration
These fields are used when generating the Remote Client configuration.
- DNS Server
- The IP address of the local DNS server will be added to the client configuration. It is initially populated using the first defined DHCP DNS Server Override address is used it found. If not, the IP address of your first non-WAN interface is used.
- Networks
- These are networks added to the client's allowed IP list. It is initially populated with all known local networks discovered from non-WAN interfaces (and their aliases) and static routes.
- Assignment
- They were used to select the method for address pool assignment. It can be set automatically to allow the system to select an unused network space or be self-assigned to configure a user-entered network space.
- Network Space
- Shows the automatically assigned networks space or allows editing the self-assigned network space.
- New Network Space
- Click when using Automatic Assignment to select a new random network space.
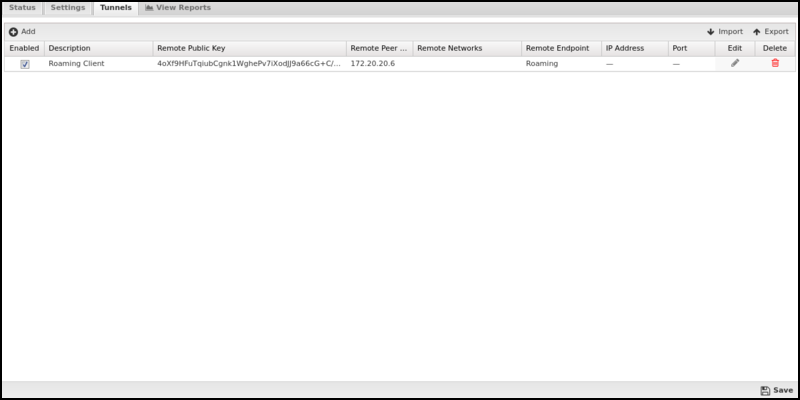
Tunnels
The Tunnels tab is where you create and manage WireGuard VPN tunnels. Each tunnel in the table can view the client configuration or edit the tunnel.
- Remote Client
- Tunnel Editor
- When you add a tunnel or edit and existing tunnel, the tunnel editor screen will appear with the following configurable settings:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enabled | This checkbox allows you to set a tunnel to enabled or disabled. |
| Description | This field should contain a short name or description. |
| Remote Public Key | This field is for the public key of the tunnel peer. |
| Remote Endpoint Type | This field controls the endpoint type for the peer.
|
| Remote Endpoint IP Address | Sets the IP address for a static endpoint. |
| Remote Endpoint Port | Sets the port for a static endpoint. |
| Remote Peer IP Address | This field sets the IP address that will be used by the remote peer. |
| Remote Networks | This field configures the list of remote networks that should be routed across this WireGuard tunnel. Networks should be entered per line in CIDR (192.168.123.0/24) format. |
| Monitor Ping IP Address | The IP address of a host on the remote network to ping for verifying that the tunnel is connected. Leave blank to disable. |
| Monitor Ping Interval | The time in seconds between attempts to ping the configured ping monitor address. |
| Monitor Alert on Tunnel Up/Down | When enabled, CONNECT and DISCONNECT alerts will be generated when the configured ping monitor transitions from reachable to unreachable and unreachable to reachable. |
| Monitor Alert on Ping Unreachable | When enabled, UNREACHABLE alerts will be generated for each monitor ping that fails when the target is unreachable. |
| Local Service Information | This section includes information from the Status tab useful when copying/pasting configurations between peers. |
WireGuard VPN client
The WireGuard Virtual Private Network client app is available for download on various mobile devices and desktop operating systems, including iOS, macOS, Android, Windows, and Linux. The download links for each supported OS are available from the WireGuard Website.
For a step-by-step setup guide, refer to the KB article Setting up WireGuard VPN on mobile devices and desktops
